About Product
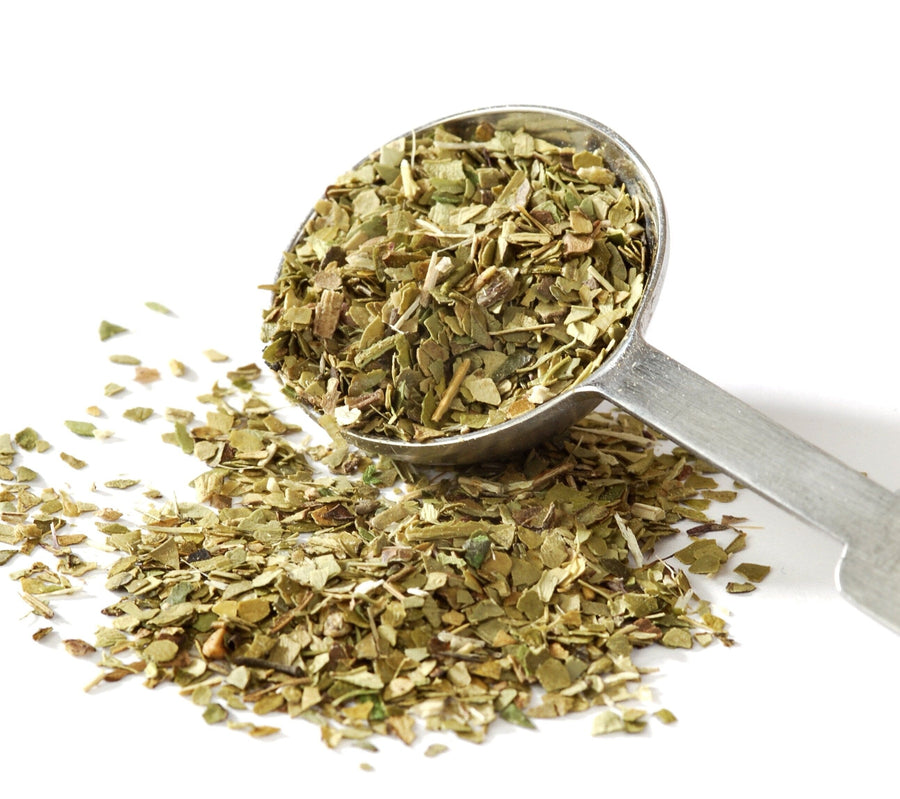
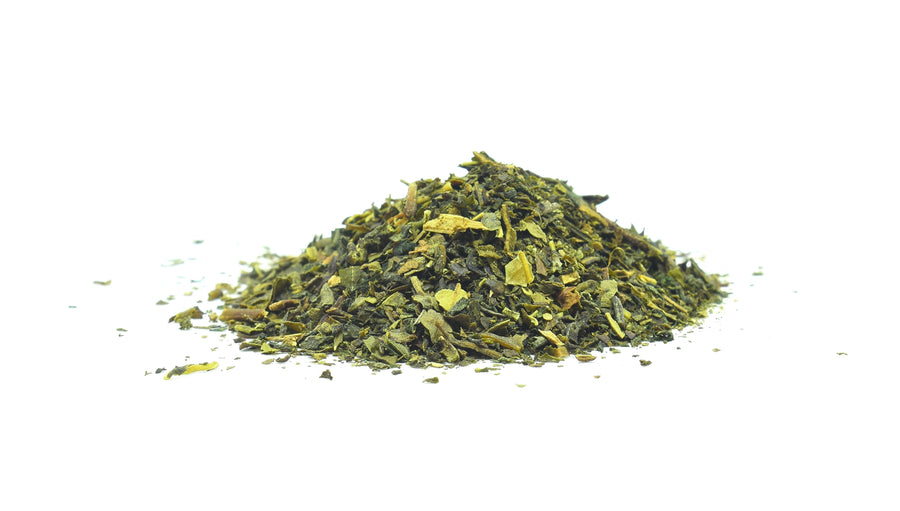
Loose Green Tea is made from carefully harvested tea leaves, offering a smooth, earthy flavor with delicate grassy notes. Traditionally enjoyed for centuries, it can be steeped to create a refreshing cup of tea with a naturally clean taste and light aroma.
Convenient and versatile, loose green tea allows you to control the strength of each brew. Perfect for hot or iced tea, it’s a timeless choice for everyday sipping and a classic addition to any tea collection.
Some research suggests that Green tea may contain the following constituents:
- Minerals: Magnesium, Phosphorus, Zinc, Manganese, Selenium
- Vitamins: Vitamin C, Thiamin, Riboflavin, Folic Acid, Beta carotene, Vitamin E
- Amino Acids: Theanine, Gaba
- Xanthine Derivatives: Caffeine, Theophylline, Theobromine, Theanine
- Phytochemicals: Polyphenols, Tannins, Flavan-3-ol, Catechin, Gallic Acid, Epicatechin, Epicatechin 3-gallate, Epigallocatechin, Epigallocatechin 3-Gallate (EGCG), 3-Gallate, Saponins, Theogallin
- Catechins: Catechin, Epicatechin, Gallocatechin, Epigallocatechin, Epicatechin gallate, Epigallocatechin gallate
- Polyphenolic Compounds: Flavanols, Flavandiols, Flavonoids
Infusion- Use the ratio of 1-2 tsp of product for every 8 ounces of distilled water. Bring water to a boil and then take off the stove. Put tea in a pot or a mug, fill it with water, and cover it for 15 minutes. (This method is specific for whole-leaf herbs and teas).
Botanical Name: Camellia sinensis.
Other Names: Camellia sinensis, Kai Hua Long Ding, Hou Kui, Camellia thea, Dragonwell Green Tea, Camellia theifera, Gunpowder, Constituent Polyphenolique de The Vert, Green Snail Spring, CPTV, Green Tip, EGCG, Epigallo Catechin Gallate, Epigallo-Catechine Gallate, Monkey Tea, Epigallocatechin Gallate, Sencha, Extrait de Camellia Sinensis, Extrait de The, Extrait de The Vert, Hyson Lucky Dragon, Extrait de Thea Sinensis, Green Sencha Tea, Green Tea Extract, Green Tea Polyphenolic Fraction, Long Jing, GTP, GTPF, Japanese Tea, Pi Lo Chun, Kunecatechins, Bancha, Poly E, Matcha, Polyphenon E, Houjicha, PTV, Kukicha, Te Verde, Genmaicha, Tea Extract, Tea Green, The, The de Camillia, Popcorn Tea, The Japonais, The Vert, The Vert de Yame, Gyokuro, The Vert Sensha, Thea bohea, Snowy Mountain Jian, Thea Sinensis, Thea Viridis, Yame Green Tea, Xin Yang Mao Jian, Yame Tea, Chinese tea, Tian Mu Qing Ding.
Ingredients: Organic Green Tea.
Origin: Grown and dried in China and packaged with care in Florida, USA.
Certifications: Certified USDA Organic.
How to Maintain Optimum Freshness
- This product is packaged in airtight stand-up, resealable foil pouches for optimum freshness.
- Once opened, push the air out of the pouch before resealing it to preserve maximum potency.
- Keep your powder in a cool, dark, dry place.
This product is 100% natural and minimally processed:
Taste, smell, texture, and color vary from batch to batch. Go here to learn why our products may naturally vary.
The important protections we take to bring you safe and nutritious superfoods:
Please go here to discover the essential steps we take to deliver fresh, quality nutrition.
Bulk Quantities?
Need to order a large quantity of our products? We are happy to help! Please get in touch with our Bulk department to discuss the details.
* Product packaging, pictures, and origin may vary.
Sources & References
1. Ahmad N et al. Cutaneous photochemoprotection by Green Tea: A brief review. Skin Pharmacol App`l Skin Physiol 2001; 14: 69-76. (ref. 4865)
2. Katiyar SK, et al. Green Tea and skin photoprotection. Cosmetics Toiletries 2001; 116 9: 69- 76. (ref. 4760)
3. Craig A, et al. Cutaneous photoprotection from ultraviolet injury by green tea polyphenols. Journal American Academy of Dermatology 2001; 44 3: 425-432. (ref. 4866)
4. Säntosh K, et al. Green tea polyphenolic antioxidants and skin photoprotection (Review).International Journal of Oncology 2001; 18:1307-1313. (ref. 4833)
5. Morganti, P, et al. New data on skin photoprotection. International Journal of Cosmetic Sciente 2000; 22 4: 305-312. (ref. 3969)
6. Säntosh K, et al. Green tea and skin. Arch Dermatol 2000; 136 8: 989-994. (ref.4867) Säntosh K, et al. Polyphenolic antioxidant Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate from Green Tea reduces UVB-induced inflammatory responses and infiltration of leukocytes in human skin. Photchemistry and Phochemistry 1999; 69 2: 148-153. (ref. 4868)
7. Guo Q, et al. Studies on protective mechanisms of four components of green tea polyphenols against lipid peroxidation in synaptosomes. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta 1996; 1304: 210-222. (ref. 2532)
8. Fourneau C, et al. Radical scavenging evaluation of green tea extracts. Phytotherapy Research 1996; 10: 529-530. (ref. 2533)
9. Morazzoni P, et al. Phytochemical anti-oxidants for cosmetic application. Agro-Food-Industry Hi-Tech 1995 : 12-16 (ref. 1996)
10. Czygan FC, et al. Herbal Drugs and phytopharmaceuticals. London :Norman Grainger Bisset, 1994; 490-492
11. Makimura M et al. Inhibitory Effect of Tea Catechins on Collagenase Activity. J Periodontol 1993; 64 7: 630-636. (ref. 1848)
12. Lunder TL. Catechins of Green Tea. Antioxidant Activity. ACS Sumposium series 1992; 507: 114-120. (ref. 1843)
13. Weisburger JH. Physiological and Pharmacological Effects of Camelia sinensis (Tea): First International Symposium. Preventive Medicine 1992; 21: 329-330. (ref. 1846)
14. Ho CT et al. Antioxidative Effect of Polyphenol Extract Prepared from Various Chinese Teas. Preventive medicine 1992; 21: 520-525. (ref. 1847)
15. Finger A et al. Chromatography of tea constituents. Journal of Chromatography 1992; 624: 293-315. (ref. 1827)
16. Wang ZY, et al. Inhibitory effect of green tea on the growth of established skin papillomas in mice Cancer Res 1992; 52 23: 6657-6665
17. Tofovic S, et al. Caffeine Potentiates Vasodilator-Induced Renin Release. The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics1991; 256 3: 850 - 860. (ref. 187)
18. March 2013, Volume 33, Issue 3, Pages 180"“187. "Green tea supplementation increases glutathione and plasma antioxidant capacity in adults with the metabolic syndrome" Authors: Basu A, Betts NM, Mulugeta A, Tong C, Newman E, Lyons TJ.
19. http://www.naturalnews.com/044667_green_tea_cognitive_function_antioxidants.html
20. http://www.eurekalert.org/pub_releases/2014-04/uob-gtb040714.php
21. http://www.naturalnews.com/028600_eye_disease_green_tea.html
22. http://science.naturalnews.com/green_tea.html
23. http://www.naturalnews.com/028877_lung_cancer_green_tea.html
24. Bruneton J. Elementos de FitoquÃmica y de Farmacognosia. Zaragoza: Acribia, 1991; 543-550. Farmacopea Francesa IX Edición. DAB 10
25. http://www.greenteahealtheffects.com/chemical-constituents.htm
26. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/1614995
27. http://umm.edu/health/medical/altmed/herb/green-tea
28. Bruneton J. Elementos de FitoquÃmica y de Farmacognosia. Zaragoza: Acribia, 1991; 543-550. Farmacopea Francesa IX Edición. DAB 10
29. https://articles.mercola.com/sites/articles/archive/2018/06/18/green-tea-boosts-heart-brain-health.aspx
30. https://www.cambridge.org/core/journals/british-journal-of-nutrition/article/effects-of-tea-intake-on-blood-pressure-a-metaanalysis-of-randomised-controlled-trials/AD10B8AF38E3184FCFDDC9778F833835
31. http://time.com/3517842/this-kind-of-tea-lowers-blood-pressure-naturally/#3517842/this-kind-of-tea-lowers-blood-pressure-naturally/
32. http://content.time.com/time/health/article/0,8599,1820250,00.html
33. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16855537
34. http://www.jbc.org/content/early/2018/05/31/jbc.RA118.002038.abstract
35. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5477123/
36. https://newatlas.com/green-tea-heart-disease-prevention/54885/
37. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20089791
38. https://www.eurekalert.org/pub_releases/2004-12/aafc-gtp112904.php
39. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21827739
40. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed?term=Epigallocatechin-3-gallate+and+postprandial+fat+oxidation+in+overweight/obese+male+volunteers&TransSchema=title&cmd=detailssearch
41. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed?orig_db=PubMed&cmd=Search&TransSchema=title&term=%22European+journal+of+clinical+nutrition%22%5BJour%5D+AND+2008%5Bpdat%5D+AND+tea
42. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed?term=%22Journal+of+agricultural+and+food+chemistry%22%5BJour%5D+AND+Green+Tea+Catechins+and+Their+Oxidative+Protection+in+the+Rat+Eye&TransSchema=title&cmd=detailssearch
43. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18515521?ordinalpos=23&itool=EntrezSystem2.PEntrez.Pubmed.Pubmed_ResultsPanel.Pubmed_RVDocSum
44. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22020144
45. https://www.precisionnutrition.com/rr-green-tea-hazards
46. https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2005/01/050128221248.htm
47. https://www.globalhealingcenter.com/natural-health/green-tea-benefits/
48. https://www.perio.org/consumer/green-tea
49. https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2007/11/071113163016.htm
50. https://www.natural-holistic-health.com/health-benefits-of-matcha-tea-how-to-make-matcha-tea/
51. https://www.news-medical.net/news/2007/04/30/24367.aspx
52. http://www.jneurosci.org/content/25/38/8807?maxtoshow=&HITS=10&hits=10&RESULTFORMAT=&fulltext=green+tea&andorexactfulltext=and&searchid=1127403163954_5553&stored_search=&FIRSTINDEX=0&sortspec=relevance&resourcetype=1&journalcode=jneuro
53. https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/322006.php
* Reviews & Success Stories Disclaimer
Product reviews solely reflect the views and opinions expressed by the contributors and not those of Z Natural Foods. Z Natural Foods does not verify or endorse any claims made in these reviews. Statements have not been evaluated by the FDA and are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease or health condition.REFERRAL PROGRAM
Share your personal link to your friends and welcome them with rewards. Claim yours when they make their first purchase.
GIVE
$10 off discount

GET
$10 off discount








































































































