About Product
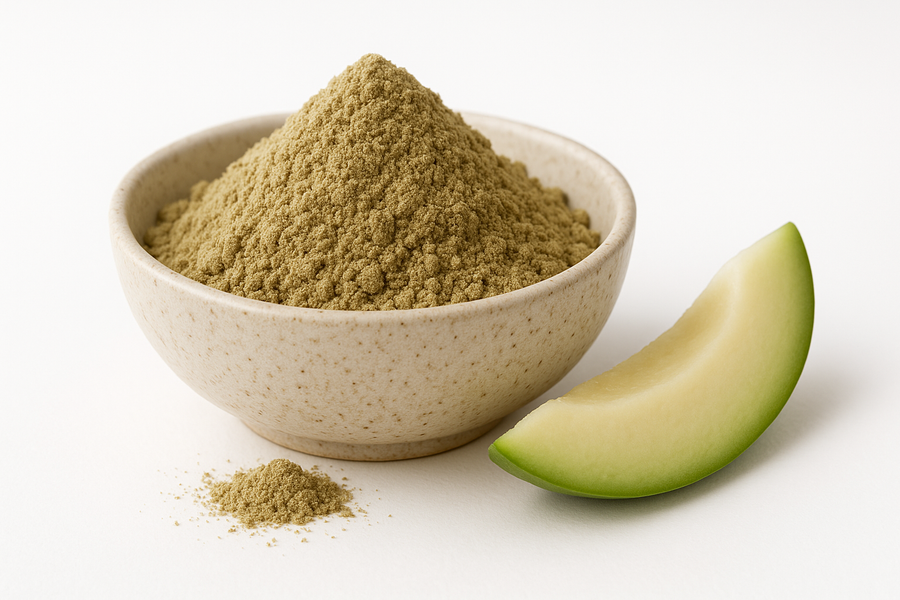
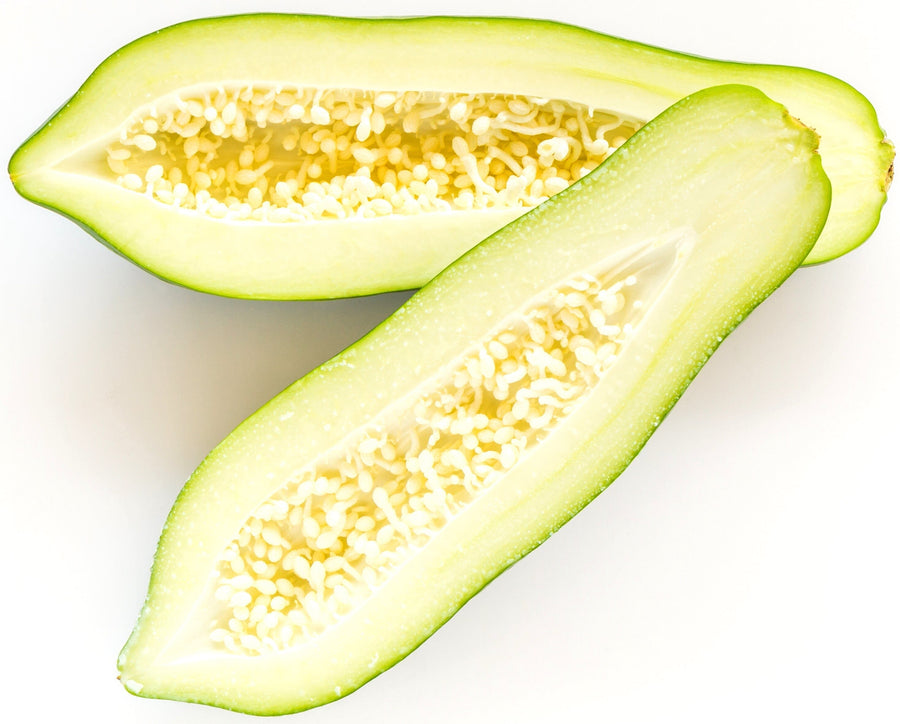
Green Papaya Powder is made from unripe papayas that are gently dried and finely ground into a smooth powder. With its mild, slightly earthy flavor, it can be blended into smoothies, teas, soups, and sauces or incorporated into baking and savory recipes.
Convenient and shelf-stable, this versatile powder is also used in some culinary and personal care applications. Its subtle taste and easy-to-use form make it a simple way to explore the unique qualities of green papaya.
- Minerals: Magnesium, Phosphorus, Zinc
- Vitamins: Vitamin C, Thiamin, Riboflavin, Niacin, Vitamin B-6, Folate, Vitamin A (RAE), Beta carotene, Vitamin A (IU), Vitamin E, Alpha Tocopherol, Vitamin K, Carotene-β Cryptoxanthin-&beta, Lutein-zeaxanthin
- Amino Acids: Arginine, Aspartic Acid, Histidine, Isoleucine, Leucine, Lysine, Methionine, Serine, Tryptophan, Valine
- Enzymes: Papain, Chymopapain
- Phytochemicals: Alkaloids, Butanoic acid, Methyl butanoate, Dehydrocarpaines, Pseudo Carpaine, Flavonols Leaves, Benzyl Glucosinolate, Alpha-phellandrene Fruit, Tannins
Suggested Use: Mix one tablespoon with juice and yogurt or add to your favorite smoothie.
Mixing suggestions: To increase flavor and nutritional profile, combine with our baobab or banana powder in a smoothie.
Botanical Name: Carica Papaya.
Other Names: Banane de Prairie, Kates, Caricae Papayae Folium, Carica papaya, Carica peltata, Carica posoposa, Chirbhita, Erandachirbhita, Erand Karkati, Green Papaya, Mamaerie, Melonenbaumblaetter, Melon Tree, Papaw, Papaya Fruit, Papayas, Papaye, Papaye Verte, Papayer, Papita, Paw Paw, Mamaeiro, Pawpaw.
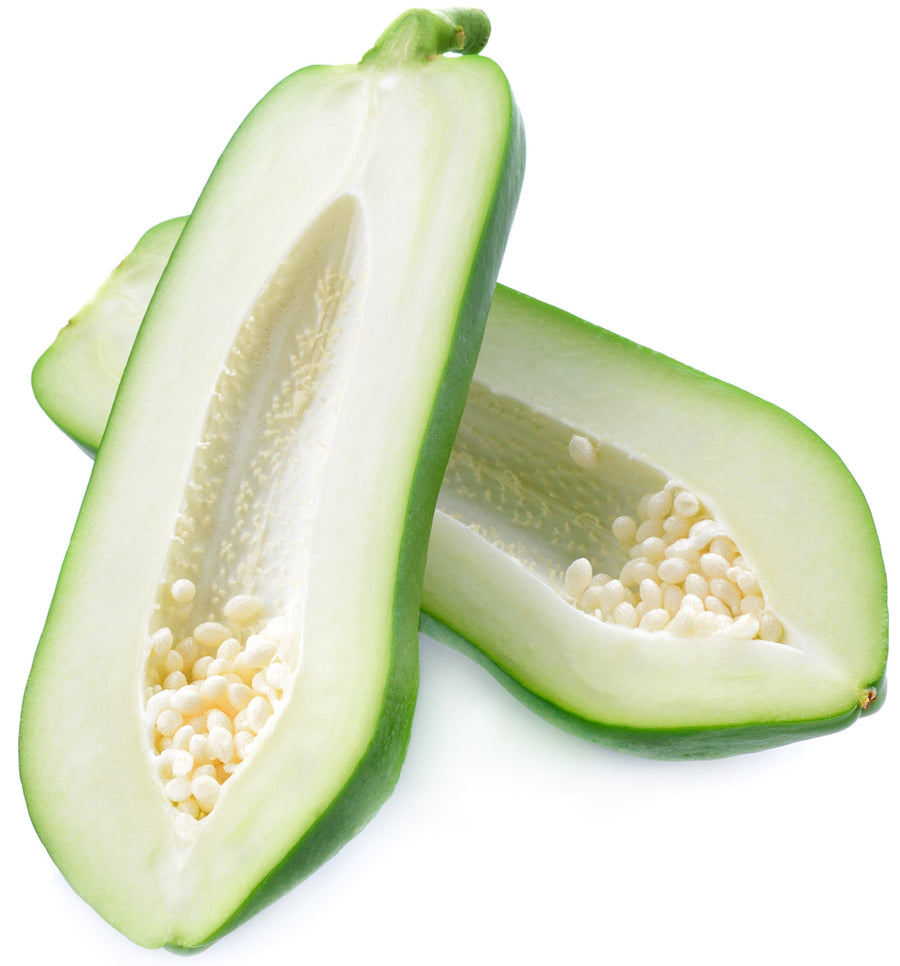
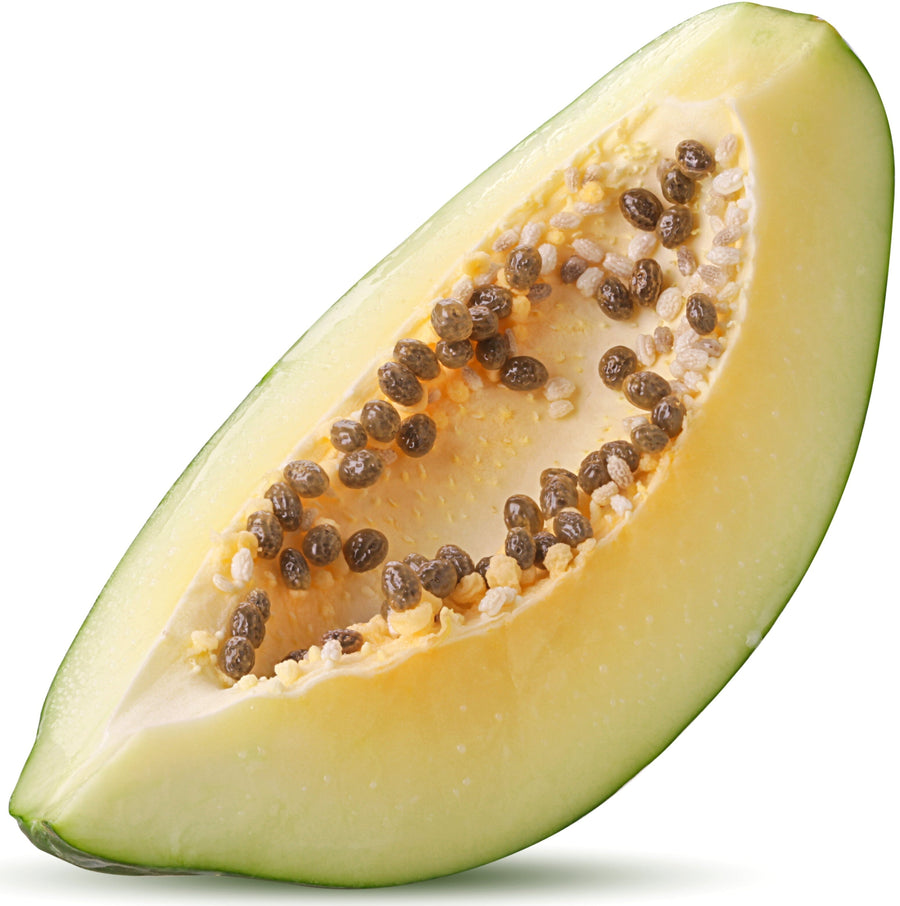
Parts Used: Whole Green Papaya, including seeds.
Ingredients: Raw Unripe Green Papaya.
Origin: Grown and dried in India and packaged with care in Florida, USA.
How to Maintain Optimum Freshness
- This product is packaged in airtight stand-up, resealable foil pouches for optimum freshness.
- Once opened, push the air out of the pouch before resealing it to preserve maximum potency.
- Keep your powder in a cool, dark, dry place.
This product is 100% natural and minimally processed:
Taste, smell, texture, and color vary from batch to batch. Go here to learn why our products may naturally vary.
The important protections we take to bring you safe and nutritious superfoods:
Please go here to discover the essential steps we take to deliver fresh, quality nutrition.
Bulk Quantities?
Need to order a large quantity of our products? We are happy to help! Please get in touch with our Bulk department to discuss the details.
* Product packaging, pictures, and origin may vary.
Sources & References
1. Cho E, Seddon JM, Rosner B, Willett WC, Hankinson SE. Prospective study of intake of fruits, vegetables, vitamins, and carotenoids and risk of age-related maculopathy. Arch Ophthalmol. 2004 Jun;122(6):883-92. 2004. PMID:15197064.
2. Ensminger AH, Ensminger, ME, Kondale JE, Robson JRK. Foods & Nutrition Encyclopedia. Pegus Press, Clovis, California. 1983.
3. Ensminger AH, Esminger M. K. J. e. al. Food for Health: A Nutrition Encyclopedia. Clovis, California: Pegus Press; 1986. 1986. PMID:15210.
4. Fortin, Francois, Editorial Director. The Visual Foods Encyclopedia. Macmillan, New York. 1996.
5. Jarvik GP, Tsai, NT, McKinstry LA, et al. Vitamin C and E intake is associated with increased paraoxonase activity. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2002 Aug 1;22(8):1329-33. 2002.
6. Jian L, Lee AH, Binns CW. Tea and lycopene protect against prostate cancer. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr. 2007;16 Suppl 1:453-7. 2007. PMID:17392149.
7. Li T, Molteni A, Latkovich P, Castellani W, Baybutt RC. Vitamin A depletion induced by cigarette smoke is associated with the development of emphysema in rats. J Nutr. 2003 Aug;133(8):2629-34. 2003. PMID:12888649.
8. Pattison DJ, Silman AJ, Goodson NJ, Lunt M, Bunn D, Luben R, Welch A, Bingham S, Khaw KT, Day N, Symmons DP. Vitamin C and the risk of developing inflammatory polyarthritis: a prospective nested case-control study. Ann Rheum Dis. 2004 Jul;63(7):843-7. 2004. PMID:15194581.
9. Rakhimov MR. Pharmacological study of papain from the papaya plant cultivated in Uzbekistan (Article in Russian). Eksp Klin Farmakol 2000 May-Jun;63(3):55-7. 2000.
10. Wood, Rebecca. The Whole Foods Encyclopedia. New York, NY: Prentice-Hall Press; 1988. 1988. PMID:15220.
11. http://canal.ugr.es/life-sciences/item/6354-scientists-decipher-fruit-tree-genome-for-the-first-time
12. "Definition of papaya in Oxford Dictionaries (British & World English)". Oxforddictionaries.com. Retrieved 2013-06-15.
13. "Merriam-Webster Online: ''pawpaw''". Merriam-webster.com. 2012-08-31. Retrieved 2013-06-15.
14. Delbridge, A., and J. R. L. Bernard. 1988 The Macquarie Concise Dictionary. The Macquarie Library: Sydney.
15. a b http://www.mhhe.com/biosci/pae/botany/botany_map/articles/article_03.html
16. "Papaya Vs Papaw". News (15 April 2005). Horticulture Australia. Retrieved 22 July 2011.
17. Sagon, Candy (13 October 2004). "Maradol Papaya". Market Watch (13 Oct 2004) (The Washington Post). Retrieved 21 July 2011.
18. " Euphytica, Volume 181, Number 2". SpringerLink. doi:10.1007/s10681-011-0388-z. Retrieved 2012-06-29.
19. "Hawaiipapaya.com". Hawaiipapaya.com. Retrieved 2013-06-15.
20. Ronald, Pamela and McWilliams, James (14 May 2010) Genetically Engineered Distortions The New York Times, accessed 1 October 2012
21. http://www.harc-hspa.com/publications/TF5.pdf
22. Danielone, a phytoalexin from the papaya fruit. Echeverri F., Torres F., Quinones W., Cardona G., Archbold R., Roldan J., Brito I., Luis J.G., and LahlouU E.-H., Phytochemistry, 1997, vol. 44, no2, pp. 255-256, INIST:2558881
23. Author: Natty Netsuwan. "Green Papaya Salad Recipe". ThaiTable.com. Retrieved 2013-06-15.
24. a b c Titanji, V.P.; Zofou, D.; Ngemenya, M.N. (2008). " The Antimalarial Potential of Medicinal Plants Used for the Treatment of Malaria in Cameroonian Folk Medicine". African Journal of Traditional, Complementary and Alternative Medicines 5 (3): 302"“321. PMC 2816552. PMID 20161952.
25. "Re:Papaya leaves for speedy rise of platelet count in Dengue" BMJ. Retrieved 2013-06-15.
26. Entry on Harrison Ford's back treatment.
27. Morton, J.F. (1987). Papaya. In: Fruits of warm climates.. pp. 336"“346.
28. Lohiya, N. K.; B. Manivannan, P. K. Mishra, N. Pathak, S. Sriram, S. S. Bhande, and S. Panneerdoss (March 2002). "Chloroform extract of Carica papaya seeds induces long-term reversible azoospermia in langur monkey" ("“ Scholar search). Asian Journal of Andrology 4 (1): 17"“26. PMID 11907624. Archived from the original on October 18, 2006. Retrieved 2006-11-18.
29. Oderinde, O; Noronha, C; Oremosu, A; Kusemiju, T; Okanlawon, OA (2002). " Abortifacient properties of Carica papaya (Linn) seeds in female Sprague-Dawley rats". Niger Postgrad Medical Journal 9 (2): 95"“8. PMID 12163882.
30. Rahmat, Asmah et al.. "Antiproliferative activity of pure lycopene compared to both extracted lycopene and juices from watermelon (Citrullus vulgaris) and papaya (Carica papaya) on human breast and liver cancer cell lines". Retrieved 9 May 2009.
31. "Papaya extract thwarts growth of cancer cells in lab tests". Retrieved 3 March 2010.
32. "The in vitro assessment of antibacterial effect of papaya seed extract against bacterial pathogens isolated from urine, wound and stool.". Retrieved 14 October 2009.
33. "Nephroprotective activities of the aqueous seed extract of Carica papaya Linn. in carbon tetrachloride induced renal injured Wistar rats: a dose- and time-dependent study". Retrieved 19 November 2009.
34. "Search the USDA National Nutrient Database for Standard Reference". Nal.usda.gov. Retrieved 2010-08-18.
35. CHOPRA, R. N. Indigenous Drugs of India, 2nd Edition, U.N. Duhr. Pub. Calcutta, India. Pp.319-321
36. DUKE, James A. Handbook of Enemy Crops, unpublished. 1933.
37. HULME. A. C. The Biochemistry of Fruits And Their Products, Volume One. Academic Press, New York. Pp. 4, 149, 523.
38. QUISUMBING. E. Medicinal Plants of the Philippines, Bureau of Print. Manila, Philippines, 1951. Pp. 632-637.
39. RAMASWAMY. A. S. and SIRSI, M. Antitubercular Activity of Some Chemical Constituents From Higher Plants Ind. J. of Pharmacy. 22(2): 34-35.
40. THORSON'S EDITORIAL BOARD. The Complete Raw Juice Therapy, THORSON'S/ Harper Collins Publishers. London, England, 1977, ·1989. Pp. 53, 33-89.
41. TWITCHELL, Paul Herbs: The Magic Healers, 2nd Edition, ECKANKAR, Menlo Park, California, 1971, 1936. Pp. 50, 94-95.
42. General and Specific References: These statements have not been evaluated by the FDA (Food and Drug Administration). This information is intended for educational and health promoting purposes only. It is not designed to diagnose, prescribe for, treat, or cure disease, illness, or injury. Any interpretation other than that is a willful misrepresentation of this information. For adverse health conditions, please consult with a qualified physician, herbalist, Naturopathic Doctor, or other Health Care Practitioner.
43. LOPEZ, D.A., M.D., WILLIAMS, R. Michael., M.D.. Ph.D.. and MIEHLKE, M., M.D. Enzymes--The Fountain Of Life. The Neville Press, Inc. Charleston, South Carolina, 1994.
44. MOWREY, Daniel B. The Scientific Validation of Herbal Medicine, Keats Publishing. Inc., New Canaan, Connecticut, 1966. Pp. 74-75.
45. SANTILLO, Humbart, B.S., M.H., Food Enzymes-The Missing Link to Radiant Health Hohm Press, Prescott Valley, Arizona, 1967
46. Berrin, Katherine & Larco Museum. The Spirit of Ancient Peru:Treasures from the Museo Arqueológico Rafael Larco Herrera. New York: Thames and Hudson, 1997.
47. http://www.medicalhealthguide.com/articles/papaya.htm
48. http://www.ars-grin.gov/duke/
49. http://ndb.nal.usda.gov/ndb/foods
* Reviews & Success Stories Disclaimer
Product reviews solely reflect the views and opinions expressed by the contributors and not those of Z Natural Foods. Z Natural Foods does not verify or endorse any claims made in these reviews. Statements have not been evaluated by the FDA and are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease or health condition.REFERRAL PROGRAM
Share your personal link to your friends and welcome them with rewards. Claim yours when they make their first purchase.
GIVE
$10 off discount

GET
$10 off discount




































































































































